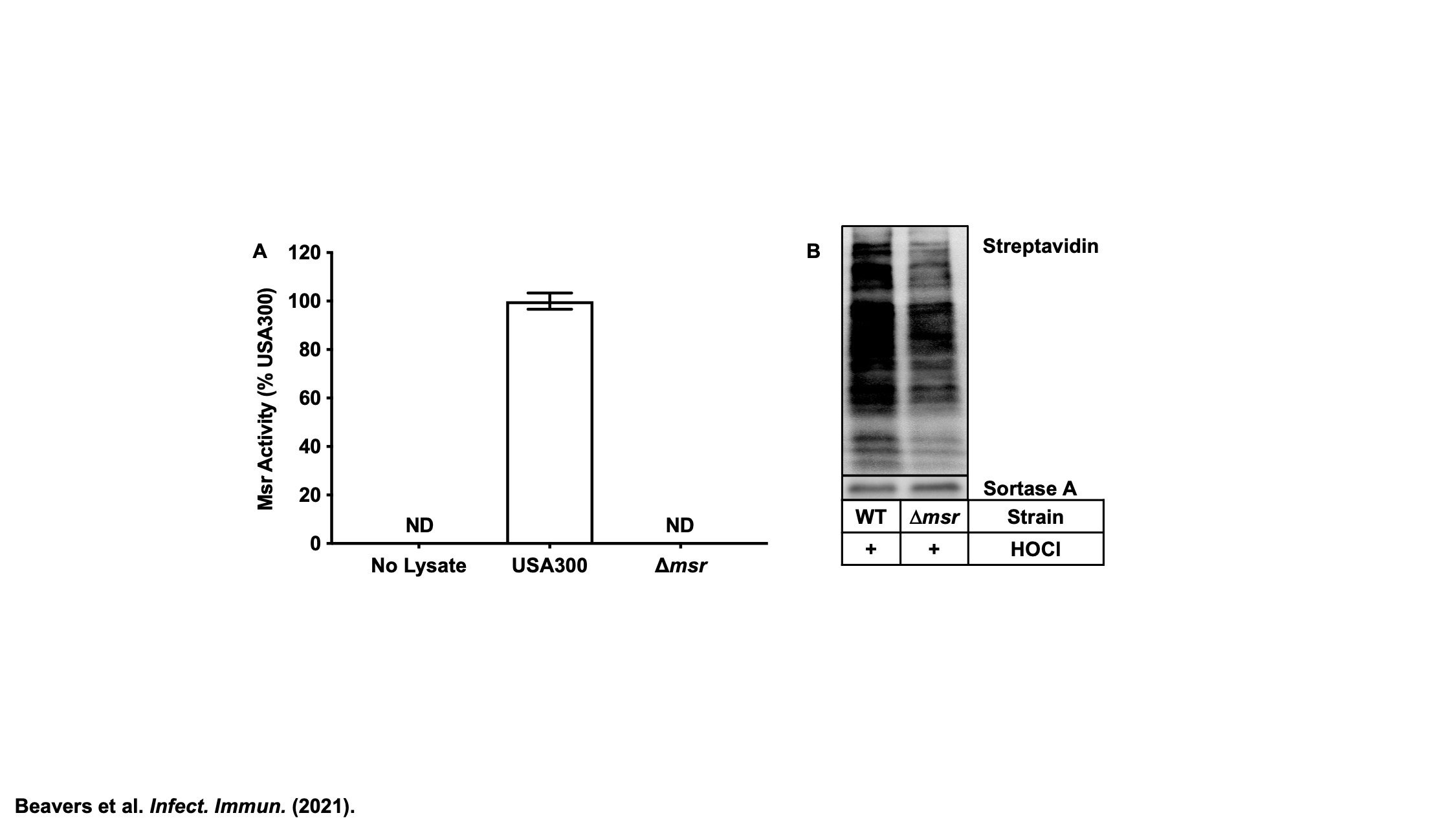
Methionine sulfoxide reductases (Msr) repair oxidized methionine residues (methionine sulfoxide) in S. aureus. (A) All four Msr enzymes were deleted in USA300 LAC to create Δmsr and the Msr enzymatic activity of the strains was quantified. No activity is detected in the Δmsr strain, indicating that there are no additional Msr enzymes in S. aureus. (
B) Neutrophils generate HOCl, a bactericidal oxidant, through the enzymatic activity of myeloperoxidase. USA300 wildtype and Δmsr were treated with HOCl in vitro. Using Ox4, a probe that reacts with methionine, but not methionine sulfoxide, the extent of methionine oxidation was measured by attaching biotin through Cu-mediated click chemistry to Ox4 modified proteins, followed SDS-PAGE, and visualization with a streptavidin-based fluorophore. A darker signal indicates less methionine oxidation, and as expected, Δmsr, which is unable to repair methionine sulfoxide has increased methionine oxidation compared to USA300 wild type.