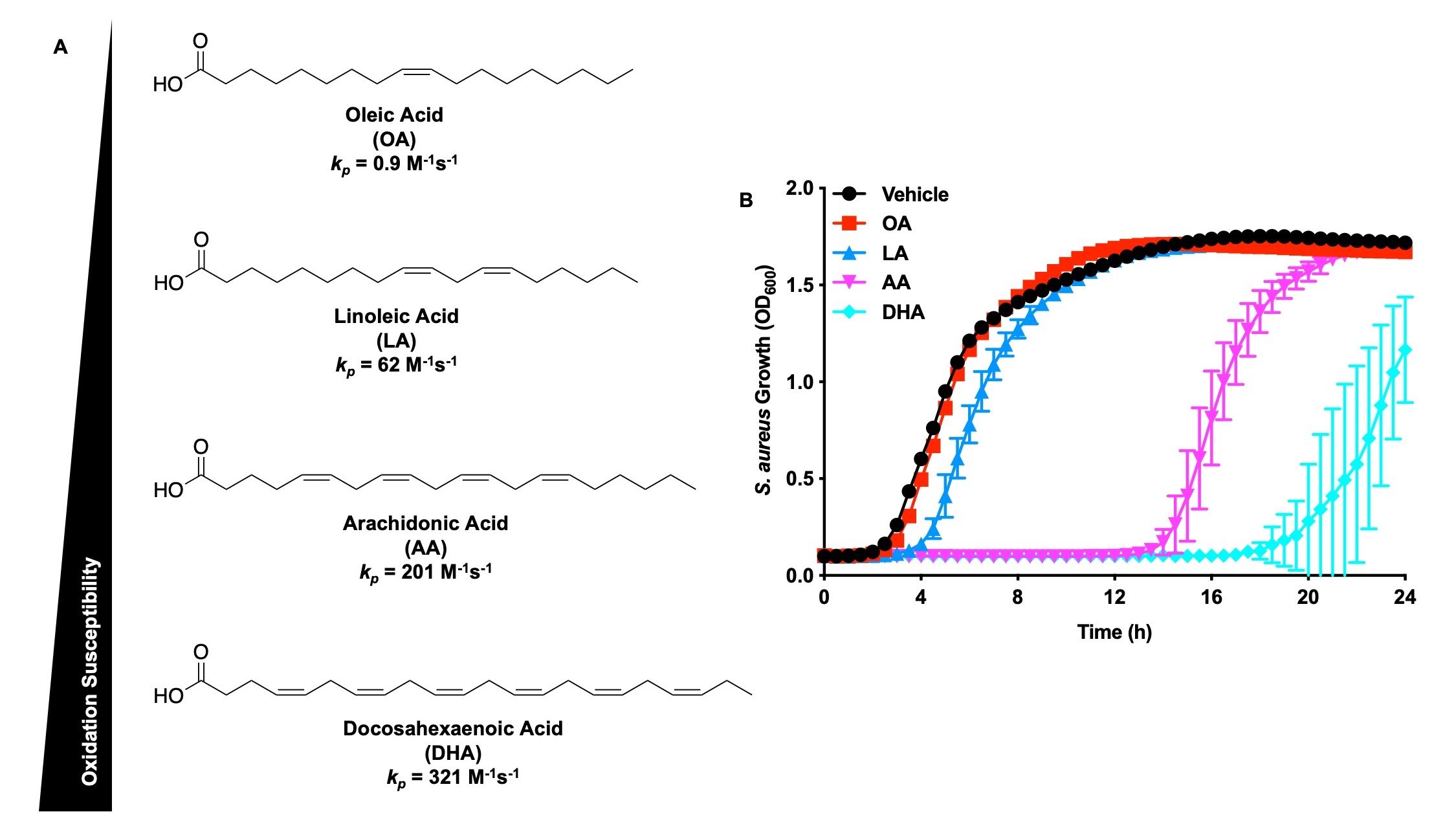
While much of the work in the group focuses on the role of arachidonic acid in controlling S. aureus infections, all tested polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) kill S. aureus. (A) PUFAs are susceptible to oxidation primarily at the bis-allylic carbons (R1-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-R2). As the number of bis-allylic carbons increase, the rate constant for the propagation of lipid peroxidation (kp) increases. The kp can be considered a measurement of how susceptible a fatty acid is to autoxidation. (B) All PUFAs that we tested kill S. aureus, but not all PUFAs kill S. aureus to the same degree. The kp value is predictive of how well a particular PUFA will kill S. aureus, further emphasizing that PUFAs kill S. aureus through an autoxidation mechanism.